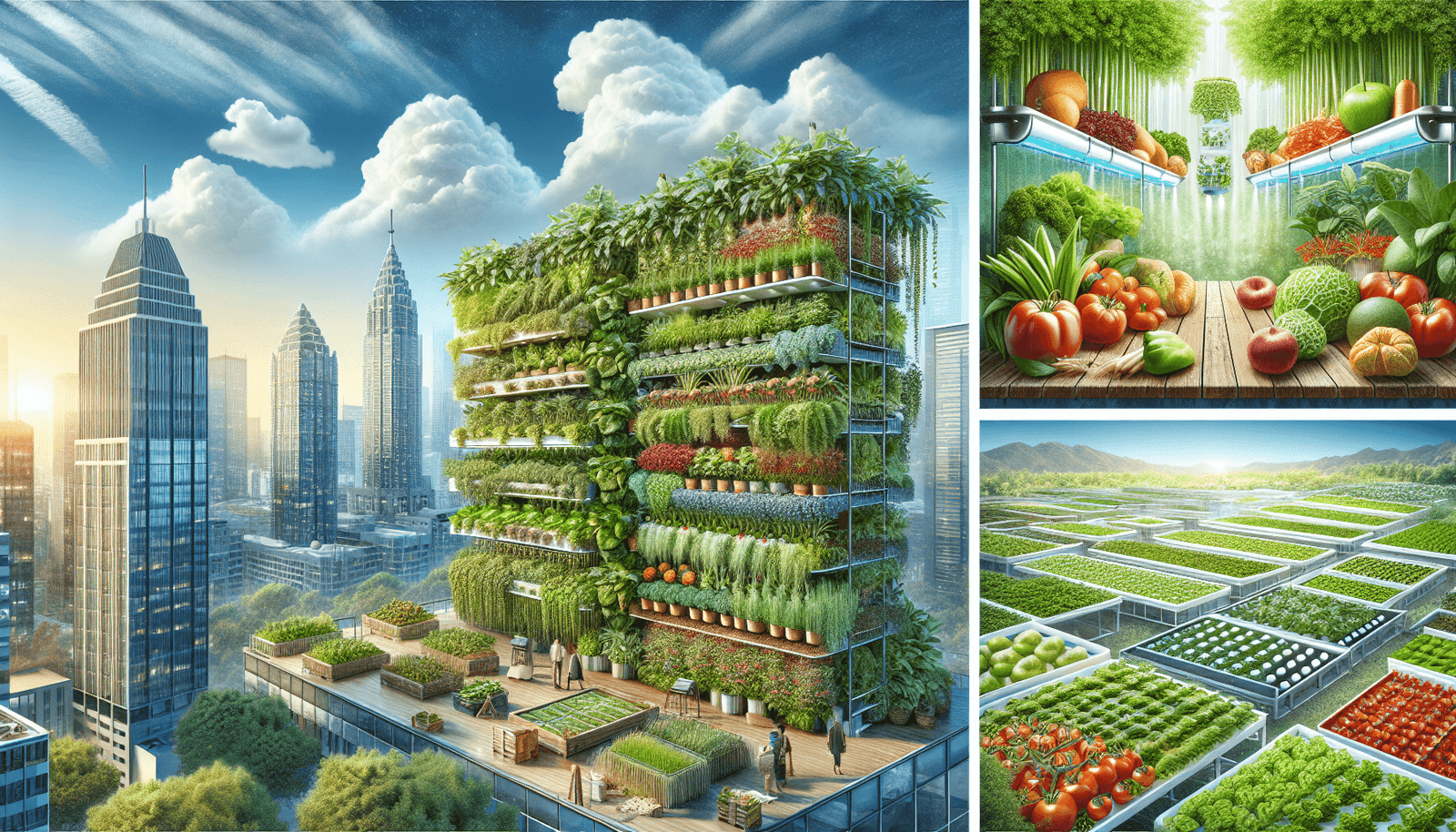
Imagine transforming a concrete jungle into a thriving green oasis that provides fresh, nutritious food for its inhabitants. As urban populations continue to rise, the demand for sustainable food production in cities becomes ever more pressing. So, how can you grow food in an urban environment? From vertical gardens clinging to skyscrapers to community gardens sprouting in vacant lots, this article explores the innovative techniques and initiatives that are revolutionizing urban agriculture, making it possible to cultivate crops on urban rooftops, walls, and even indoors. Discover the incredible ways in which urban dwellers are reconnecting with nature and redefining what it means to be a city farmer.

The Benefits of Growing Food in Urban Areas
Provides Access to Fresh and Nutritious Food
Growing food in urban areas provides an excellent opportunity for individuals to have access to fresh and nutritious food. In cities, it can be challenging to find affordable and high-quality produce. However, by growing your own food, you have direct control over the cultivation process, ensuring that your fruits and vegetables are free from harmful chemicals and pesticides. Additionally, urban farming allows you to choose a wide variety of plant species, including heirloom and rare varieties that may not be readily available in supermarkets.
Promotes Sustainability and Environmental Conservation
Urban farming plays a vital role in promoting sustainability and environmental conservation. By growing food locally, it reduces the need for long-distance transportation, thus minimizing carbon emissions and reducing the overall environmental footprint. It also helps to combat deforestation and land degradation caused by traditional agriculture. Additionally, urban farming often employs sustainable practices such as composting and water-efficient irrigation techniques, contributing to the overall conservation of resources.
Encourages Community Engagement and Social Connections
Another significant benefit of urban farming is the encouragement of community engagement and social connections. Community gardens and shared urban spaces provide individuals with the opportunity to come together, share knowledge, and collaborate on gardening projects. This fosters a sense of belonging and camaraderie within the community, promoting mental well-being and social interactions. Furthermore, urban farms often organize events, workshops, and educational programs, creating a platform for people of different backgrounds to connect and learn from one another.
Factors to Consider in Urban Food Growth
Available Space
When considering growing food in an urban environment, the availability of space is a crucial factor. Unlike rural areas, urban landscapes often have limited space for gardening. However, even in small areas, innovative gardening techniques such as container gardening, vertical gardening, and utilizing unused spaces can maximize the productivity of the available area. It is essential to evaluate the available space and plan accordingly to optimize crop yields.
Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight exposure is vital for the growth and development of plants. However, tall buildings, trees, and other structures in urban areas can cast shadows and limit the amount of sunlight reaching your crops. Assessing the direction and duration of sunlight in your urban space is crucial in determining what crops will thrive and selecting suitable gardening methods that can maximize sunlight exposure.
Soil Quality
The quality of soil in urban environments may vary significantly due to factors such as pollution, construction, and industrial activities. Conducting a soil test to assess its composition and fertility is vital before starting your urban farm. In cases where soil quality is poor, remedial measures such as adding compost, organic matter, or using raised beds can help create a suitable growing environment.
Water Supply and Drainage
Having a reliable water supply is essential for successful urban farming. Ensure access to a water source, whether it be through a tap or rainwater harvesting system. In urban areas, water runoff and drainage can be challenging due to impermeable surfaces. Implementing proper drainage techniques, such as raised beds and permeable surfaces, can help prevent waterlogging and ensure water is utilized effectively by the crops.
Potential Contamination Risks
Urban environments may present contamination risks, such as heavy metal contamination from industrial activities or chemical pollutants. Conducting soil tests and researching the history of the land can help identify any potential risks to food safety. Implementing proper soil remediation techniques, such as phytoremediation, and practicing good crop management strategies can mitigate these risks and ensure the production of safe and healthy food.
Container Gardening in Urban Environments
Choosing Suitable Containers
Container gardening is an excellent option for urban environments with limited space. When choosing containers, it is important to consider factors such as size, material, and drainage. Opt for containers that are appropriately sized for the plants you wish to grow, ensuring enough room for root development. Materials such as terracotta, plastic, or fabric pots are popular choices for container gardening. Additionally, ensure that containers have proper drainage holes to prevent waterlogging.
Selecting the Right Soil Mix
The soil mix used in container gardening should be well-suited for the plants’ growth and provide proper drainage. A quality potting mix that is lightweight, well-draining, and nutrient-rich is ideal. Avoid using garden soil, as it can become compacted and hinder root development in containers. Consider adding organic matter, such as compost or coconut coir, to improve moisture retention and nutrient availability in the soil mix.
Picking the Appropriate Plants
When selecting plants for container gardening in urban environments, choose varieties that are well-suited for confined spaces and have a compact growth habit. Herbs, salad greens, cherry tomatoes, peppers, and dwarf fruit trees are excellent options for container gardening. Consider the space available, sunlight exposure, and the specific needs of the plants when making your selections.
Proper Watering Techniques
Container plants can dry out quickly, especially in urban environments where there may be higher temperatures and wind exposure. It is essential to establish a regular watering schedule while being mindful not to overwater. Monitor the moisture level of the soil by sticking your finger into it. If it feels dry at a depth of an inch, it is time to water. Consider using watering cans or drip irrigation systems for efficient and targeted watering.
Providing Adequate Sunlight
Most container plants require a minimum of six hours of direct sunlight per day. Place your containers in areas that receive ample sunlight or utilize balcony railings, windowsills, or rooftop spaces to maximize sunlight exposure. If sunlight is limited, consider using supplemental grow lights to provide the necessary light for your plants’ growth.
Vertical Gardening in Urban Spaces
Utilizing Wall-Mounted Planters and Trellises
Vertical gardening is an effective way to maximize space utilization in urban areas. Wall-mounted planters and trellises can be used to grow climbing plants such as peas, beans, cucumber, and vine tomatoes. Attach these structures to walls or fences, taking care to ensure proper support and stability. Vertical gardening not only saves space but also creates an aesthetically pleasing green backdrop in urban environments.
Plant Selection for Vertical Growth
When selecting plants for vertical gardening, choose vining or trailing varieties that naturally grow upwards. These plants have the ability to climb or trail along trellises or structures. Some popular choices include pole beans, sweet peas, indeterminate tomatoes, and certain types of cucumbers. Ensure that the trellis or support structure is appropriately sized and strong enough to handle the weight of the plants as they grow.
Addressing Watering and Drainage Needs
In vertical gardening, proper watering and drainage are essential. Consider using watering systems such as drip irrigation or soaker hoses to ensure the water reaches the plants’ roots. Regularly check the moisture levels in the soil and adjust the watering schedule accordingly. Adequate drainage is crucial to prevent water buildup, which can lead to root rot and fungal diseases. Ensure that the structures are designed to allow excess water to drain away effectively.
Maximizing Sunlight Exposure in Limited Spaces
In urban environments with limited space, maximizing sunlight exposure becomes crucial for vertical gardening. Position your vertical garden structures in areas that receive the most sunlight, such as south-facing walls or balconies with ample sunlight exposure. Regularly monitor the amount and duration of sunlight received by the plants and make adjustments as necessary. Supplemental grow lights can also be used to ensure the plants receive adequate light, especially in shaded areas or during the winter months.

Hydroponics and Aquaponics Systems in Urban Agriculture
Understanding Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponics is a soil-less cultivation technique that involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions. In urban agriculture, hydroponics offers several advantages, including the efficient use of water and nutrient resources and the ability to grow plants vertically or in confined spaces. Basic hydroponic systems include nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and vertical towers. Understanding the principles and requirements of different hydroponic systems is essential before setting up your own urban hydroponic farm.
Setting up an Aquaponics System
Aquaponics combines hydroponics with fish farming, creating a symbiotic relationship between the plants and fish. Fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter and purify the water for the fish. Setting up an aquaponics system in an urban environment requires careful planning and consideration of factors such as tank size, balance between fish and crop ratios, water pH levels, and temperature control. Researching and consulting aquaponics experts or attending workshops can provide valuable guidance for beginners.
Maintaining Proper Nutrient Levels
In hydroponic and aquaponics systems, maintaining proper nutrient levels is crucial for the plants’ health and growth. Regularly monitoring and adjusting the nutrient solution’s pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and nutrient concentrations ensure that the plants receive optimal nutrition. Utilize specialized nutrient solutions or prepare your own hydroponic nutrient mixes based on the specific requirements of the plants being grown.
Monitoring Water Quality in Aquaponics
In aquaponics systems, monitoring water quality is essential for both the plants and fish. Regularly test water parameters such as pH, ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and dissolved oxygen levels to ensure a healthy environment for both components of the system. Adequate filtration and aeration systems should be in place to maintain water quality. Continuous monitoring and adjustments are necessary to optimize the performance and productivity of the aquaponics system.
Rooftop Farming and Green Roofs
Benefits and Challenges of Rooftop Farming
Rooftop farming offers numerous benefits in urban areas, including maximizing underutilized space, reducing the urban heat island effect, and improving air quality. It allows for the production of fresh food in close proximity to consumers, reducing transportation distances and carbon emissions. However, rooftop farming also presents challenges such as load capacity limitations, access to water, and potential structural modifications required. Evaluating the feasibility and addressing these challenges are crucial for successful rooftop farming endeavors.
Evaluating Roof Load Capacity
Before initiating rooftop farming, it is important to evaluate the load capacity of the rooftop to ensure it can support the weight of the farming infrastructure, including soil, containers, and irrigation systems. Consulting with a structural engineer or building professional is recommended to assess the structural integrity of the rooftop and determine any necessary reinforcements or modifications.
Structural Considerations and Reinforcements
Depending on the rooftop’s structure, additional reinforcements may be required to support the weight of the farming infrastructure. This may involve reinforcing walls, beams, or adding support columns. Working with a professional contractor or engineer experienced in rooftop farming can help ensure the structural integrity and safety of the rooftop farming setup.
Selection of Suitable Crops
When choosing crops for rooftop farming, consider the microclimate and environmental conditions specific to the rooftop. Factors such as sunlight exposure, wind, and temperature variations should be taken into account. Hardy and drought-tolerant crops such as herbs, salad greens, dwarf fruit trees, and succulents are well-suited for rooftop environments. It is also essential to consider factors such as maintenance requirements, water requirements, and the potential for wind or pest damage when selecting suitable crops.

Community Gardens in Urban Areas
Establishing a Community Garden
Community gardens provide a platform for individuals to come together, share resources, and cultivate their own food in a shared space. Establishing a community garden involves several important steps, starting with obtaining permission from the relevant authorities or landowners. Forming a committee or group to organize and manage the garden’s operations, developing a set of guidelines or bylaws, and securing necessary funding or sponsorship are also crucial for a successful community garden.
Organizing and Managing Garden Plots
In a community garden, organizing and managing individual garden plots is essential to ensure fairness and maximize utilization of space. Establish a clear system for assigning plots, whether through a lottery or a first-come, first-served basis. Communicate gardening guidelines, including expectations for maintenance, organic practices, and shared resource management. Encouraging regular communication and organizing communal events or workdays can foster a sense of community and shared responsibility among gardeners.
Promoting Inclusive and Diverse Participation
Community gardens thrive when they are inclusive and diverse, providing opportunities for individuals of all backgrounds to participate. Implement outreach and educational programs to engage communities that may face barriers to accessing fresh food or green spaces. Collaborate with local organizations, schools, and community groups to promote involvement and create an inclusive and welcoming environment for all gardeners.
Addressing Security and Vandalism Concerns
While community gardens can be immensely rewarding, they may also face security and vandalism concerns, especially in urban areas. Establishing security measures such as fencing, locks, and surveillance cameras can help deter vandalism and unauthorized access. Encouraging community involvement and organizing events that showcase the benefits of the garden to the neighborhood can also foster a sense of ownership and discourage vandalism.
Utilizing Indoor Growing Systems
Using Artificial Lighting for Indoor Gardens
Indoor gardening provides a solution for urban environments with limited outdoor space or restrictive climates. Artificial lighting is a crucial component of indoor gardening setups, as it provides the necessary light spectrum for plant growth. LED grow lights are a popular choice due to their energy efficiency and customizable light spectra. Position the lights at an appropriate distance from the plants to ensure optimal light intensity and duration, following the specific requirements of the plants being grown.
Understanding Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) refers to the practice of growing crops indoors in controlled environments, optimizing temperature, humidity, light, and nutrient levels. CEA technologies include hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics, which allow for year-round cultivation and precise control over growing conditions. Understanding the principles of CEA and implementing appropriate technologies and practices can result in higher yields and better quality produce in urban indoor gardens.
Optimizing Temperature and Humidity Levels
Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels is crucial for indoor gardening success. Most plants thrive in temperatures between 65-75°F (18-24°C), although specific crop requirements may vary. Utilize thermostats and humidity meters to monitor and control these factors. Ventilation systems, humidifiers, and dehumidifiers can be employed to modify the indoor environment as needed.
Maintaining Proper Air Circulation and Ventilation
Proper air circulation and ventilation are key to prevent the buildup of stagnant air, disease, and pest problems in indoor gardens. Install fans or ventilation systems to ensure constant airflow, promoting transpiration and reducing the risk of mold or fungal growth. Regularly clean and maintain ventilation systems to prevent dust accumulation, which can impede airflow and negatively impact plant health.

Utilizing Unused Spaces for Urban Farming
Converting Vacant Lots into Productive Gardens
Transforming vacant lots into productive gardens is a creative way to utilize underutilized urban spaces. With permission from the relevant authorities, vacant lots can be cleaned, cleared of debris, and prepared for cultivation. Implementing methods such as raised beds, container gardening, or vertical gardening can further optimize space utilization. Engage with the local community, organizations, and volunteers to ensure the long-term maintenance and sustainability of the garden.
Implementing Vertical Farming in Abandoned Buildings
Abandoned buildings can be repurposed into vertical farming facilities, offering an opportunity to grow food indoors on a larger scale. Vertical farming involves stacking layers of plants vertically in controlled environments with artificial lighting and hydroponic or aeroponic systems. Retrofitting abandoned buildings with the necessary infrastructure such as lighting, grow systems, and climate control requires careful planning, collaboration with experts, and securing funding or grants.
Recycling Containers and Materials for Growing Food
In urban farming, recycling containers and materials for growing food is a sustainable and cost-effective approach. Reusing materials such as plastic buckets, wooden pallets, or discarded containers can be repurposed into planters or raised beds. Upcycling materials not only reduces waste but also provides an opportunity for creative and innovative gardening techniques. When repurposing materials, ensure that they are clean, free from toxic substances, and suitable for the specific needs of the crops being grown.
Challenges and Solutions for Urban Food Production
Land and Space Limitations
Land and space limitations are common challenges faced in urban food production. However, innovative gardening methods such as container gardening, vertical gardening, and utilizing underutilized spaces can help overcome these limitations. Maximizing space utilization, utilizing rooftop and vertical farming techniques, and engaging the community in shared gardening initiatives can make more efficient use of the available land in urban areas.
Access to Water Resources
Access to water resources can be limited in urban environments. Utilizing methods such as rainwater harvesting, implementing water-efficient irrigation systems (such as drip irrigation), and using low-flow fixtures can help conserve water. Additionally, exploring partnerships with local water authorities or conserving and reusing water through techniques such as aquaponics can help mitigate water resource challenges in urban food production.
Managing Pests and Disease in Urban Environments
Urban environments can present unique challenges when it comes to managing pests and disease. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices, including biological controls, organic pesticides, and regular scouting for pests, can help manage pest populations effectively. Implementing good hygiene practices, such as sterilizing gardening tools, rotating crops, and using disease-resistant plant varieties, can minimize the risk of plant diseases in urban farming.
Ensuring Nutritional Diversity and Food Security
Ensuring nutritional diversity and food security in urban food production is crucial. It requires the selection of a wide range of crops that provide essential nutrients and a balanced diet. Engage with the community in educational programs that promote awareness of the importance of diverse diets and the nutritional value of locally grown produce. Collaborate with local food banks, schools, or organizations to tackle food insecurity issues by donating surplus produce or organizing programs that aim to provide fresh food to underserved populations.
In conclusion, growing food in urban areas offers numerous benefits, including access to fresh and nutritious food, sustainability, and social connections. When embarking on urban farming, it is important to consider factors such as available space, sunlight exposure, soil quality, water supply, and potential contamination risks. Utilizing various techniques such as container gardening, vertical gardening, hydroponics, and aquaponics allows for productive urban agriculture in confined spaces. Rooftop farming, community gardens, indoor growing systems, and the utilization of unused spaces are innovative solutions to maximize food production in urban environments. Despite challenges such as land limitations, water resources, pests, and nutritional diversity, urban food production can be successful with proper planning, community engagement, and sustainable practices. By embracing urban farming, you can enjoy the benefits of growing your own fresh produce while contributing to healthier communities and a more sustainable future.